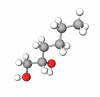
Sucrose is an organic compound that is common in most households. Most people know it simply as sugar, the white granules that they mix with food to add a sweet taste. In typical form, it is an odorless powder.
Sucrose is a type of carbohydrate known as a disaccharide. The molecular formula for the substance is 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms. Its fundamental components, however, are the monosaccharides glucose and fructose. The former is the molecule used by the human metabolism to generate energy.
Sucrose is typically derived for consumption from beets or sugarcane. However, there is a tariff on imports of this substance in the United States. The most common sweetener used in that country is high fructose corn syrup. Nevertheless, sucrose is sold in bulk quantities in supermarkets.
Sucrose is a sweet additive for any meal. However, overuse of this and other sweeteners is tied to high obesity rates and diabetes among other diseases.In skin care applications, Sucrose is used for its moisturizing properties, thanks to numerous hydroxyl groups in the structure it captures water molecules and enhances skin's moisture retention. Breaking down into glucose and fructose molecules, it energizes skin cells stimulating their functions. Some manufacturers claim that sucrose can accelerate the skin desquamation process by acting as an exfoliating agent.